- Addresses no longer need to be activated
- Recommended Use of Address Transfer
Blockchain development so far, there are two different bookkeeping models: UTXO and Account. UTXO has characteristics such as statelessness, while facing the increasingly strong personalized business needs, the expression ability is relatively poor; Account model has the advantage of programmability, and can change the user’s on-chain status through smart contract language. Starcoin based on Account model, made some interesting design, through the smart contract language Move to the on-chain account bookkeeping operations, so that the user’s data is more secure.
1. Addresses no longer need to be activated
Starcoin supports two ways of initializing accounts.
actively initializing the on-chain account and activating the address.
passively initializing the on-chain account, where the address no longer needs to be activated.
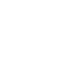
The following diagram shows the complete process of actively creating an Account through the Starcoin wallet.
- Generate Mnemonics: Starcoin wallet follows BIP32, BIP39, BIP44 specifications and can generate Mnemonics very reliably to manage wallet accounts.
- Generate secret key pairs (Private Key, Public Key): Starcoin keys are generated using the Ed25519 curve and PureEdDSA scheme, see RFC 8032.
- Generate Authentication Key: SHA3-256 (Public key | 0x00), where | is the connection. 0x00 is a 1bytes identifier, indicating a single signature. This will be described in detail later.
- Generate the account address (Address): the last 16 bytes of the Authentication Key.
- Generate Receipt Identifier: See sip-21 for more details.
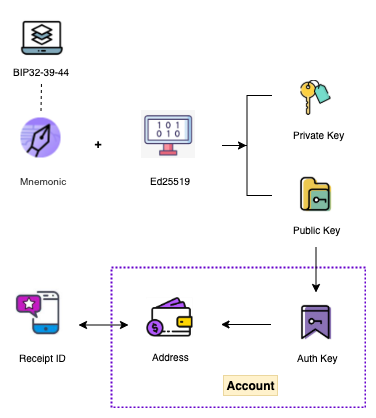
In the process of creating an account above, the purple dotted line indicates the process of initializing the account on-chain, i.e., activating the chain address. This is the active way to initialize the account and requires an Authentication Key to initialize the on-chain account. In the case that users are used to using Address, this approach increases the complexity of the operation and the cost of understanding for users. The on-chain account Account initialized using this approach can be simply understood as Address + Authentication Key, as shown in the figure.
On June 15, 2021, Starcoin completed its first upgrade since the launch of the main network. This upgrade contains several optimizations (proposal details), one of the very important updates is the addition of a new way to passively initialize accounts, where addresses no longer need to be activated, simplifying the account initialization process. Users can initialize their accounts while knowing only the Address (and not the Authentication Key). This approach conforms to the user’s operating habits and reduces the cost of the operation, while shielding the Authentication Key details from the user. A typical application scenario is to transfer funds to an Address that does not exist on-chain. The on-chain account Account initialized using this approach can be simply understood as Address + Default Authentication Key, as shown in the figure.

Upgrading from the active to the passive method, the Address no longer needs to be activated. Although the Authentication Key is set to the default value 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000, it will be set to the correct value at some point in the future (when the first transaction initiated by the current account is on-chain). Now, Starcoin users are completely free to choose any method to initialize their on-chain account.
2. Role of Authentication Key
In the above process, the role of the Authentication Key is not reflected; in fact, the role of the Authentication Key is to authenticate transactions. As shown in the figure.
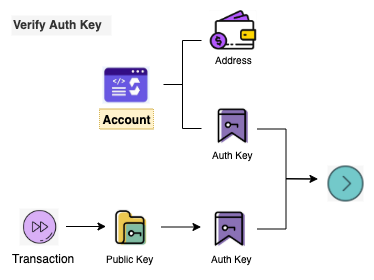
During the authentication phase of the transaction, the Authentication Key contained in the transaction must be equal to the Authentication Key saved on-chain for that account, that is, for the transaction to continue to be executed. In fact, the Public Key can also serve this purpose, and the reason for adding the Authentication Key starts with Starcoin’s Account, which has some unique features, including a very interesting design that does not distinguish between single-signature and multi-signature accounts. Starcoin’s multi-signature is done in the wallet, using the Public Key array (a single-signature account can be understood as an array with only 1 element) to calculate the Address, as shown in the figure.
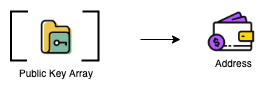
So, in the absence of Authentication Key, the on-chain Account can be simply understood as Address + Public Key Array, as shown in Fig.

The length of the Public Key array is not fixed, which will increase the storage space of the Account and also increase the complexity of transaction authentication, so Starcoin’s Account uses a fixed length Authentication Key. This is the role and benefit of the Authentication Key. To sum up, the advantages of Authentication Key for verifying transactions are.
- fixed length.
- separation of the Account from the multi-signature logic.
3. Setting the Authentication Key for the first time
The passive initialization of the Account method, which occurs when Account A creates Account B using Address, means that Account B does not exist on-chain. So as long as the default value of Authentication Key is identified and set to the correct value when the new Account B executes its first transaction, it is fully compatible with the whole process, as shown in the figure.
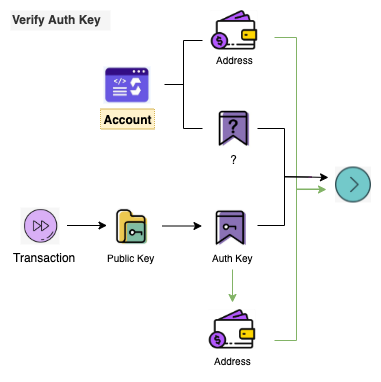
The green line part of the diagram indicates that if the Authentication Key of the account on-chain is the default value, the Address calculated by the Authentication Key of the transaction must be equal to the Address saved on-chain of the account before the transaction can continue to be executed. After the transaction is executed, the correct Authentication Key will be saved under the account on-chain, completing the Authentication Key setup.
4. Recommended Use of Address Transfer
A typical application scenario was mentioned earlier, transferring funds to an Address that does not exist on-chain.
Prior to the June 15, 2021 upgrade (proposal details), since Starcoin accounts had to be activated before transfers could be made, and an Authentication Key was required to activate the account, a Receipt Identifier was designed to be compatible with the non-existent account, containing the Address and optionally The Receipt Identifier contains the Address and optionally the Authentication Key.
After the June 15, 2021 upgrade, Starcoin accounts can be created based on Address and no longer need to be activated. Therefore, even if an account does not exist on-chain, it is possible to use Address to transfer funds directly.
Starcoin recommends users to use the more convenient Adress for transferring funds (0x address). As the upgrade is a compatibility upgrade, addresses starting with stc can also continue to be used, but they are no longer recommended.